What Are Innovation Pathways?
Innovation pathways describe the processes through which research and innovation (R&I) evolve from initial ideas into concrete, impactful solutions. These pathways encompass the development, implementation, communication, dissemination, and exploitation of knowledge, data, tools, and practices. They are the basis by which scientific results and innovative approaches are translated into effective responses to societal challenges.
In the context of climate change and cultural heritage,innovation pathways are particularly critical. They enable the adaptation and protection of cultural and natural heritage— tangible, intangible, and natural—to increasing hydroclimatic stressors such as floods, droughts, and heatwaves.
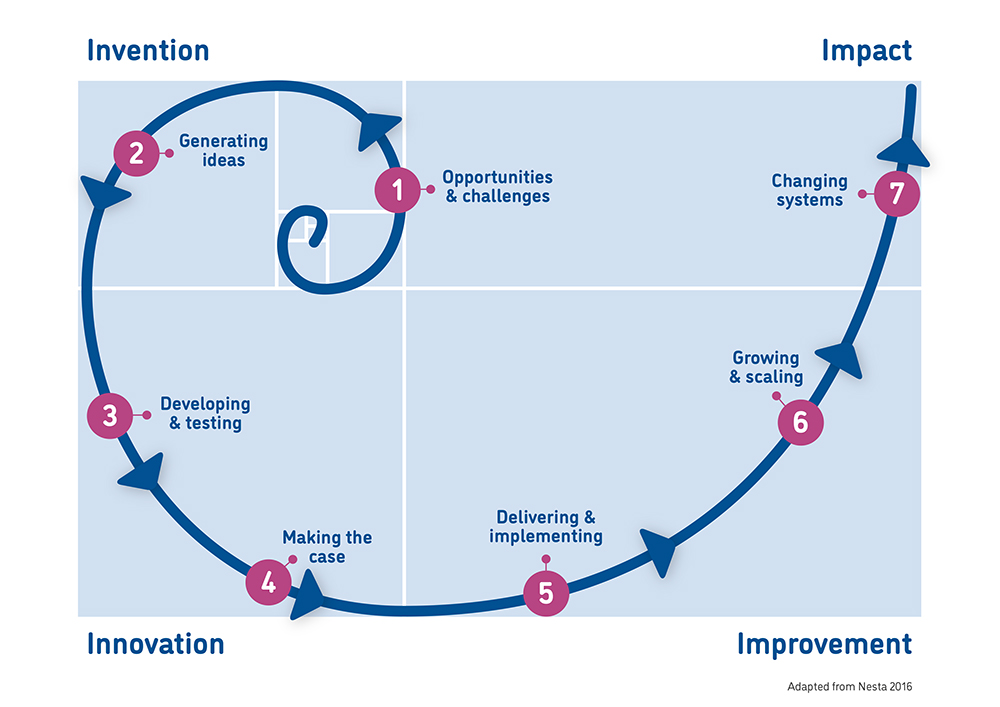
Drawing from conceptual frameworks in sustainability transitions and systems innovation, and building on the Nesta Innovation Spiral (Figure 1), SD-WISHEES understands innovation as a dynamic, multi-stage process, ranging from opportunity identification and idea generation to implementation, scaling, and systemic change.
Four types of Innovation Pathways
Within this framework, SD-WISHEES identifies four interlinked types of pathways:
● Technology development and adoption – fostering new tools, methods, and technologies that support adaptation and resilience.
● Capacity development – strengthening institutional, professional, and community competencies to apply innovations effectively.
● Policy influence – shaping regulatory, planning, and governance processes using R&I evidence.
● Fostering enabling environments – enhancing the institutional, financial, and social conditions needed to sustain innovation over time.
These categories are not mutually exclusive. Like the broad focus of R&I, they frequently overlap and reinforce each other across an iterative, often non-linear journey, from idea generation to the proposed systems-level change

Innovation Pathways in the
SD-WISHEES Project
SD-WISHEES (Supporting and Developing WIdening Strategies to tackle Hydroclimatic Extreme Events: impact and Sustainable solutions for cultural heritage) addresses the urgent need to protect cultural heritage from the growing impacts of climate extremes. Its core objective is to improve the interface between science, policy, and society by advancing and scaling up effective innovation pathways.
Work Package 6, and specifically Task 6.1, provides a foundational review and analysis of how R&I efforts—past and present—have led to the protection and sustainable management of cultural heritage in diverse contexts. By systematically examining instruments, mechanisms, and strategies already in use, SD-WISHEES aims to:
● Identify innovation pathways with proven or promising potential for uptake and scaling.
● Understand enabling conditions and persistent barriers.
● Inform future stakeholder engagement and co-design of solutions.
● Contribute to European and international objectives, including the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The project's methodological approach combines a structured desk review of scientific and grey literature with expert interviews. This has produced a robust evidence base of innovation pathways relevant to cultural heritage and climate adaptation, particularly regarding hydroclimatic extremes.

©2025 CNR, All Rights Reserved.





